A til Å-guide til digital transformasjon i produksjonsindustrien (med eksempler)
Nittiåtte prosent av produsentene planlegger å implementere eller har allerede implementert strategier for nettsalg. Hva er drivkraften bak den digitale transformasjonen i industrien?
Produsenter erkjenner at kundene er avgjørende for deres suksess, noe som gjør en forbedret kundeopplevelse til den drivende faktoren for å implementere digital transformasjon.
Så hva er digital transformasjon i industrien, og hvordan kan du lykkes med å utnytte den? La oss finne ut av det.
De viktigste poengene:
- Digital transformasjon i produksjonen utnytter ny teknologi ved å implementere den i alle deler av virksomheten, enten det gjelder produksjonsprosessen, arbeidsstyrken, sluttproduktet eller markedsføring og salg.
- Fordelene ved å ta i bruk additiv produksjon er blant annet raskere byggetider, muligheten til å produsere mer innovativ design uten å øke kostnadene og å skape lettere, men mer robuste og holdbare produkter.
- Produksjonsanalyse fanger opp og analyserer data for å forutsi etterspørsel, forebygge feil, utføre forebyggende vedlikehold, optimalisere priser og gjøre forbedringer der det trengs.
Hva er digital transformasjon i produksjonsindustrien?
Digital transformasjon i produksjonsindustrien omfatter mer enn markedsføring og salg i digitale kanaler, selv om det er en del av prosessen. Produsenter drar nytte av ny teknologi ved å implementere den i alle deler av virksomheten, enten det gjelder produksjonsprosessen, arbeidsstyrken eller sluttproduktet.
Målet med digital transformasjon innen produksjon er å
- Maksimere inntektene ved å forbedre driftseffektiviteten og merkevarebevisstheten
- Forbedre kvaliteten på de produserte produktene
- Forbedre kundeopplevelsen for å oppnå et konkurransefortrinn
- Forbedre virksomhetens adopsjoner med datadrevet beslutningstaking
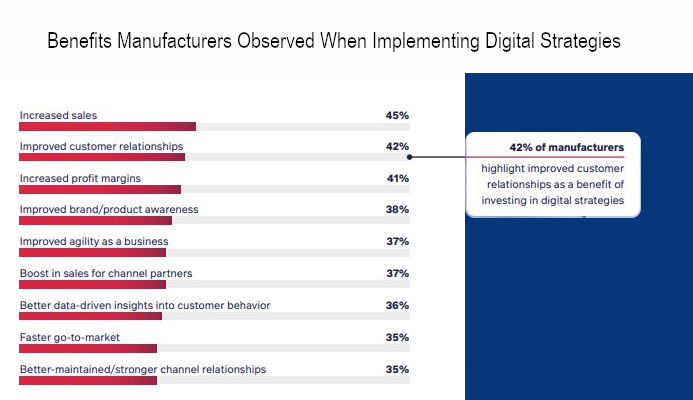
5 eksempler på digital transformasjon i produksjonsindustrien
Nå som vi har forstått definisjonen av og fordelene med digital transformasjon, skal vi se nærmere på fem områder der produsenter kan utnytte den nyeste teknologien til å forbedre virksomheten.
1. Additiv produksjon
Hva er dette? Additiv produksjon, ofte omtalt som 3D-printing, er en prosess som skaper et fysisk objekt ut fra en digital design. Vanligvis bruker ingeniører CAD-programvare (Computer-Aided Design) til å tegne tegningen. Deretter tar en utskriftsmaskin designet og skriver ut gjenstanden i det materialet som passer best til bedriftens formål. Alternativene inkluderer, men er ikke begrenset til, plast, metall, karbonfiber, harpiks og papir.
I tradisjonell produksjon tar arbeideren en blokk med materiale, for eksempel tre eller metall, og skjærer, hugger og meisler til produktet er ferdig. Additiv produksjon har fått navnet sitt fordi ingenting blir fjernet, bare lagt til for å skape gjenstanden.
Fordelene med additiv produksjon er blant annet raskere byggetider, muligheten til å produsere mer innovative design uten å øke kostnadene og å skape lettere, men likevel mer robuste og holdbare produkter.
Et eksempel: Resolution Medical er et Minnesota-basert selskap som lager medisinsk utstyr ved hjelp av additiv produksjon. Tidligere brukte de sprøytestøping for å produsere et produkt, men selskapet oppdaget fordelene ved å 3D-printe dem i stedet. De nevner raskere time-to-market og fleksible designendringer som fordeler ved å gå over til additiv produksjon.
2. Digital tvilling
Hva er dette? Digital tvillingteknologi bruker data fra sensorer som er koblet til maskiner og verktøy på produksjonslinjen, til å generere en virtuell modell av et virkelig produkt, en produksjonsprosess eller et helt system. Den digitale modellen er en nøyaktig kopi med alle dimensjoner, driftsverdier og oppførsel som det virkelige produktet eller miljøet ville hatt. Når ingeniørene er fornøyde med den virtuelle modellen, bygger de den fysiske modellen. Når produktet eller systemet er i produksjon, fortsetter den digitale versjonen å eksistere side om side med den fysiske.
Digital tvillingteknologi hjelper bedrifter med å identifisere problemer før de oppstår, noe som i sin tur forbedrer eksisterende produkter, drift og tjenester.
Et eksempel: Unilever PLC har åtte digitale tvillinger i Nord-Amerika, Sør-Amerika, Europa og Asia. IoT-sensorene leverer sanntidsdata som temperatur og motorhastighet til Unilevers bedriftssky på hvert sted. Den digitale tvillingen simulerer intrikate hva-hvis-scenarioer for å finne de beste driftsparameterne. Resultatet er at selskapet bruker materialer mer presist og begrenser avfall fra varer som ikke oppfyller kvalitetsstandardene.
3. E-handel
Hva er dette? E-handel er salg og kjøp av produkter eller tjenester gjennom digitale kanaler. Det er mange aspekter ved e-handel som produsenter kan optimalisere. Kan du for eksempel inkludere salg direkte til forbrukere i tillegg til salg til forhandlere? Er nettstedet ditt mobilvennlig? Kan du skape en personlig kundeopplevelse, for eksempel ved å sende dem en e-post når det kommer en oppdatering av et produkt du vet de liker?
Et eksempel: Wastequip, en produsent av avfallshåndteringsutstyr, opprettet et brukervennlig nettsted der kundene enkelt kan søke, legge inn en bestilling og spore kjøpene sine. Dette skrittet i den digitale transformasjonen resulterte i en åttedobling av nettrafikken for selskapet.
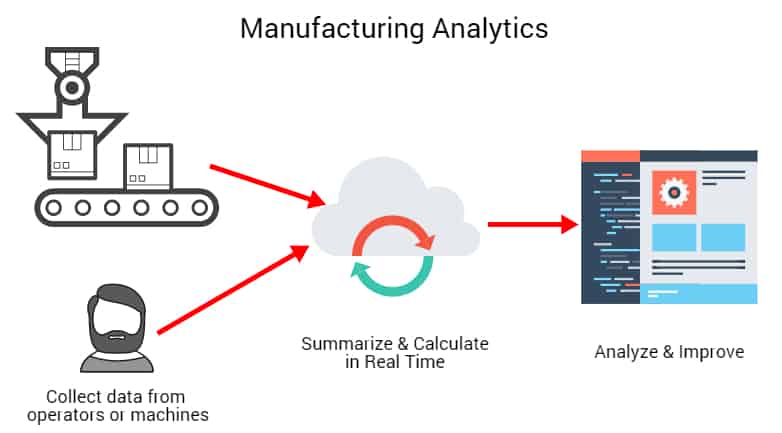
4. Produksjonsanalyse
Hva er dette? Produksjonsanalyse samler inn all informasjon (ved hjelp av programvare) fra maskiner og arbeidere i alle produksjonsfaser frem til et produkt kommer ut på markedet. Produksjonsanalyse fanger opp og analyserer dataene for å forutsi etterspørsel, forebygge feil, utføre forebyggende vedlikehold, optimalisere priser og gjøre forbedringer der det trengs.
Produsenter kan samle inn data fra robotikk, sensorer, IIoT-enheter (Industrial Internet-of-things) og ERP-programvare (Enterprise Resource Planning).
Et eksempel: Konux, en tysk produsent av jernbaneinfrastruktur, bruker produksjonsanalyse til kapitalforvaltning og prediktivt vedlikehold. Resultatet er at selskapet har redusert vedlikeholdskostnadene med 25 % og minimert antallet feil som forårsaker forsinkelser.
5. Automatisering av robotiserte prosesser
Hva er dette? Robotisert prosessautomatisering (RPA) bruker roboter til repeterende oppgaver for å frigjøre menneskelige medarbeidere til mer komplekst arbeid. Fordelene med RPA er blant annet
- Sparer tid og menneskelig arbeidskraft på monotone oppgaver
- Raskere lanseringstid på markedet
- Minimere behandlingsfeil
Noen scenarier der RPA er nyttige, er
- Behandling av fakturaer
- Svar på forespørsler om tilbud
- Generering av lagerrapporter
Et eksempel: Xcel Energy, en leverandør av elektriske tjenester, brukte RPA til å overvåke datalageret til kjernekraftdivisjonen. Ved å utnytte automatisering for å overvåke, varsle og håndtere feil, reduserte selskapet antallet personer som håndterer datalagerprosesser, betraktelig.
Dyk ned i den digitale transformasjonen med Optimizely
Optimizelys programvareløsninger og ekspertteam kan hjelpe deg gjennom hele din digitale transformasjonsreise. Vi gir deg en datadrevet beslutningsstrategi for å forbedre produksjonsvirksomheten din og kundenes opplevelse av virksomheten din.
Ta kontakt med Optimizelyi dag for å se hvordan vi kan hjelpedeg på veien mot digital transformasjon .
- Last modified:25.04.2025 21:15:12